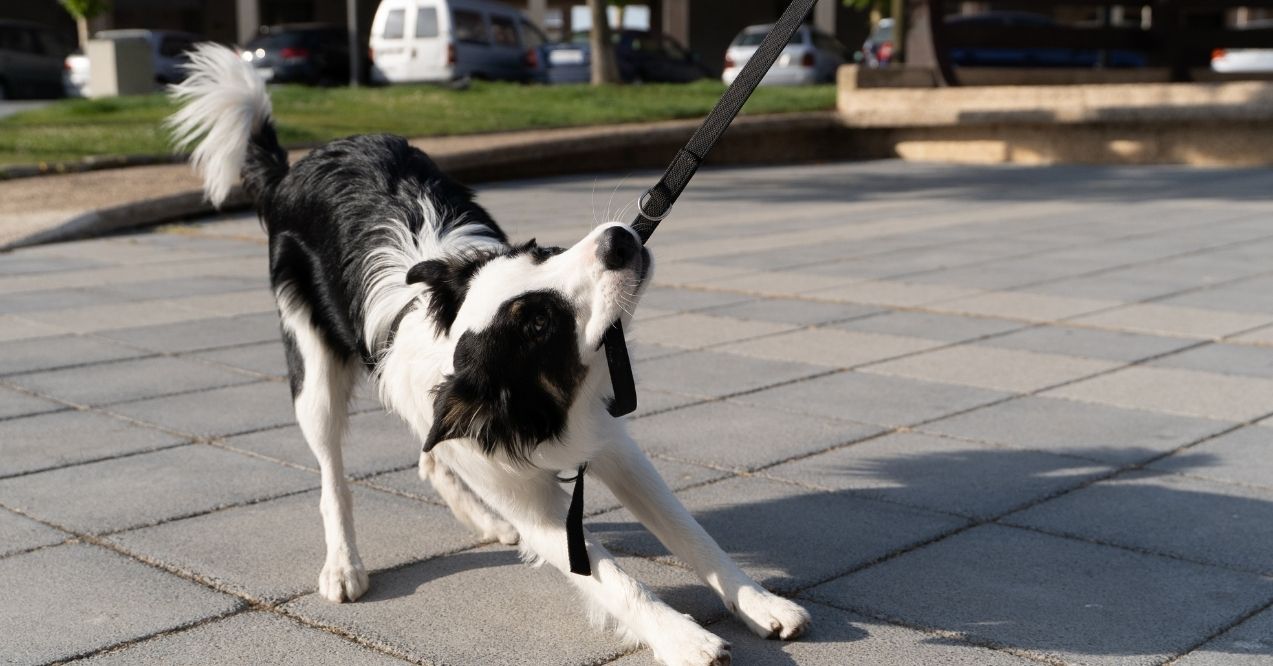
How to Stop Your Dog From Biting the Leash
Picture this: you’re excited for a peaceful walk with your dog, but within minutes, your furry companion turns the leash into their personal chew toy. What should be a relaxing stroll becomes a frustrating tug-of-war session. You’re not alone in this struggle – leash biting is one of the most common walking challenges dog owners face.
This behavior stems from understandable causes, from excitement and energy to anxiety and natural instincts. Learning how to stop dog from biting leash requires understanding your dog’s motivations and applying the right techniques consistently.
This guide provides practical strategies tailored to different training stages, breed characteristics, and emotional needs. With patience and the right approach, you can transform your walks into the peaceful, bonding experiences they’re meant to be.
Why Dogs Bite the Leash
Understanding dog biting leash behavior starts with recognizing that this action serves different purposes for different dogs. The reasons behind this habit can vary significantly based on your dog’s breed, age, and current emotional state.
Common Behavioral Triggers
Several key factors drive leash biting behavior in dogs:
- Playfulness – Dogs view the moving leash as an exciting toy, especially during energetic moments
- Frustration – Feeling restricted or overstimulated during walks leads to redirected energy toward the leash
- Stress displacement – When encountering triggers like other animals or loud noises, dogs bite the leash instead of addressing the actual stressor
This behavior pattern helps explain why do dogs bite themselves in other situations, as dogs often redirect uncomfortable feelings toward accessible objects or even their own bodies when overwhelmed.
Breed-Specific Instincts
Different breeds show distinct leash biting patterns:
- Herding breeds (Border Collies, Australian Shepherds) – Nip at leashes due to natural drive to control movement
- Working breeds (German Shepherds, Rottweilers) – When a dog bites leash repeatedly, it often signals boredom or excess energy
- Toy breeds (Chihuahuas, Yorkies) – Bite from anxiety or feeling vulnerable during outdoor encounters
Life Stage Influences
Age significantly impacts leash biting motivations:
- Puppies – Bite from curiosity and teething discomfort while exploring textures
- Adolescents – Display impulsive leash biting during rebellious phases, testing boundaries consistently
- Adults – Develop this habit from years of reinforcement, making it an automatic response to specific situations
How to Stop a Dog From Biting the Leash

Learning how to stop dog from chewing leash requires a combination of management techniques, redirection strategies, and environmental adjustments. The most effective approach addresses both the immediate behavior and underlying triggers that cause your dog to target the leash.
Success depends on consistency and choosing methods that match your dog’s specific motivations and energy levels.
Pause and Redirect
Stop moving immediately when your dog grabs the leash – pulling or yanking only increases their excitement and makes the “game” more appealing. Stand still and wait for your dog to release the leash naturally, then calmly say a redirect command like “look” or “sit.”
Reward the moment they focus on you instead of the leash with a high-value treat. This technique teaches your dog that leash biting stops the fun, while attention to you creates positive outcomes.
Use the Right Leash Type
Choosing the appropriate leash material can significantly impact success in learning how to stop leash biting. Heavy chewers benefit from chain or metal leashes that provide an unpleasant texture, while moderate biters often respond well to bitter apple-treated fabric leashes.
Leash Type Best For Pros Cons Chain/Metal Heavy chewers Unpleasant texture, durable Heavier, can cause injury Biothane Moderate biters Easy to clean, flexible More expensive Treated Fabric Light chewers Comfortable grip, affordable Requires reapplication
Offer a Better Outlet
Carry a designated chew toy or rope specifically for walks to redirect your dog’s biting impulse. Durable rubber toys or braided rope toys work well for satisfying the urge to bite and tug. Teach “take it” and “drop it” commands using this toy, making it more appealing than the leash through interactive play.
Pre-Walk Play and Mental Stimulation
Drain excess energy before walks through sniffing games, puzzle feeders, or indoor fetch sessions. Mental stimulation activities work as effectively as meditation for dogs, promoting calmness and focus. A tired dog with satisfied mental needs shows less interest in destructive leash behaviors during walks.
Keep Walks Calm and Predictable
Structure your walking routine to minimize triggers that escalate leash biting:
- Walk during quieter hours when fewer distractions exist
- Choose familiar routes that don’t overstimulate your dog
- Maintain consistent walking pace and direction changes
- Avoid high-traffic areas until the behavior improves
Support Through Training and Routine
Building lasting change requires consistent training methods and realistic expectations about progress. Successful leash training develops through daily practice, careful observation, and maintaining a positive mindset during challenging moments. The key lies in creating predictable routines that support both you and your dog through the learning process.
Positive Reinforcement Techniques
Reward every moment of calm walking with high-value treats and enthusiastic verbal praise. Focus on reinforcing commands like “leave it,” “heel,” or “look at me” before your dog has a chance to grab the leash.
Timing matters – deliver rewards within three seconds of the desired behavior to create clear associations. Practice these commands at home first, then gradually introduce them during walks when your dog shows signs of wanting to bite the leash.
Use of Behavior Tracking
Keep a simple journal noting when leash biting occurs, including time of day, potential triggers, and your dog’s response to redirection. Track patterns like whether incidents happen more frequently during morning walks or when encountering specific stimuli.
This information helps you anticipate challenging moments and adjust your training approach accordingly. Progress often happens gradually, and written records help you recognize improvements you might otherwise miss.
Managing Human Frustration
Leash biting can feel embarrassing in public and frustrating when progress seems slow. Remember that this behavior represents your dog’s attempt to communicate needs or manage overwhelming feelings.
Reframe training sessions as bonding opportunities where you learn to understand each other better. Your calm, patient energy directly influences your dog’s ability to learn and feel secure during walks.
Special Considerations for Puppies

Puppies present unique challenges when it comes to leash behavior, as their biting often stems from teething discomfort, curiosity, and high energy levels. Learning how to get puppy to stop biting leash requires gentler approaches that account for their developmental stage and shorter attention spans.
Gentle Puppy Training Tactics
Provide appropriate teething toys before and during walks to satisfy your puppy’s need to chew on textured objects. Use simple redirection commands like “sit” or “touch” when leash biting occurs, immediately rewarding compliance with tiny, soft treats.
Keep initial walks very short – 5 to 10 minutes – to prevent overstimulation that often triggers leash grabbing. Practice leash handling indoors first, allowing your puppy to get comfortable with the sensation before adding outdoor distractions.
Puppy Leash-Biting Prevention Plan
Establish a consistent three-step pre-walk routine that sets your puppy up for success:
Step 1 – Allow 5 minutes of supervised sniffing around your yard or entrance area to satisfy initial curiosity.
Step 2 – Practice one simple command like “sit” or “stay” with treat rewards to engage your puppy’s mind and establish focus.
Step 3 – Attach the leash calmly while your puppy is in a seated position, rewarding them for remaining still during the process.
Conclusion
Understanding how to stop dog from biting leash involves recognizing your dog’s individual triggers and applying consistent training techniques. Success comes from combining the right equipment, pre-walk preparation, and positive reinforcement methods tailored to your dog’s breed and age.
Remember that leash biting often reflects excitement, frustration, or natural instincts rather than defiance. With patience and the strategies outlined in this guide, you can transform challenging walks into enjoyable bonding experiences.
Dogs bite leashes due to excitement, frustration, boredom, or stress displacement. Playful dogs view moving leashes as toys, while anxious dogs redirect nervous energy. Breed instincts, overstimulation from outdoor triggers, and learned habits also contribute to this common walking behavior.
Provide teething toys, use gentle redirection with “sit” commands, and keep walks short to prevent overstimulation. Practice indoor leash handling first, establish pre-walk routines, and reward calm behavior immediately. Puppies need patience as they learn appropriate chewing outlets.
Leash biting typically indicates excitement, frustration, or playfulness rather than aggression. True aggression involves growling, stiff body language, and targeting people or animals. Most leash biting represents redirected energy or overstimulation, not dangerous behavioral tendencies requiring serious intervention.
Chain or metal leashes deter heavy chewers with unpleasant textures, while biothane leashes resist moderate biting and clean easily. Bitter apple-treated fabric leashes work for light biters. Choose based on your dog’s chewing intensity and comfort preferences.
Yes, mental stimulation significantly reduces leash biting by draining excess energy before walks. Puzzle feeders, sniffing games, and trick training create mental fatigue similar to physical exercise. A mentally satisfied dog focuses less on destructive behaviors during outdoor activities.
Advertisement. This site offers health, wellness, fitness and nutritional information and is designed for educational purposes only. You should not rely on this information as a substitute for, nor does it replace, professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. If you have any concerns or questions about your health, you should always consult with a physician or other health-care professional. Do not disregard, avoid or delay obtaining medical or health related advice from your health-care professional because of something you may have read on this site. The use of any information provided on this site is solely at your own risk.